Author:
-
Position:
General Manager of Foreign Trade Department, Taojun Refrigeration -
Professional Experience:
Engaged in international trade within the refrigeration industry since 2004.
Expert in brand strategy and omni-channel marketing, having led three multi-million yuan projects that boosted brand exposure by over 200%.
-
Core Competencies:
Proficient in data analysis and user growth strategies.
Skilled in SEO/SEM and social media management tools.
Experienced in cross-departmental collaboration and team leadership.
-
Philosophy:
"Data-driven decisions, creativity-powered branding." Committed to achieving business value and user experience excellence through refined operations. -
Vision:
Eager to collaborate with partners to explore emerging market opportunities and set industry benchmark cases.
Contact Us to Find More Products
what is Single row wire tube condenser?
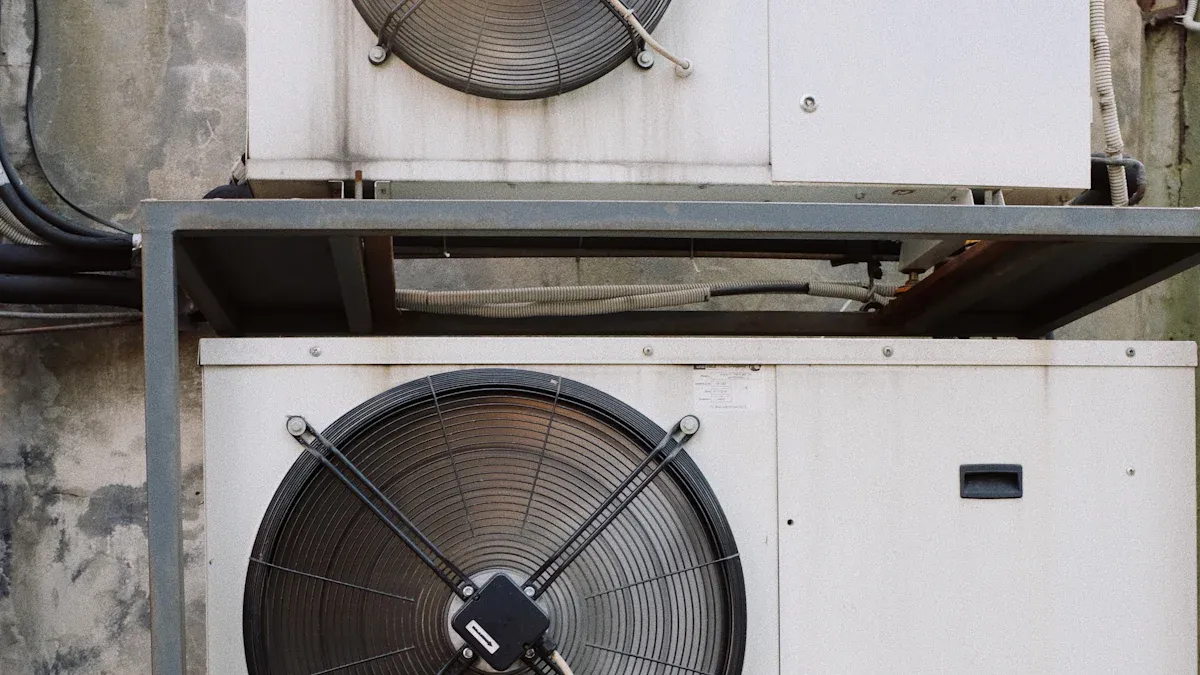

A single row wire tube condenser is a crucial component in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. The single row wire tube condenser utilizes a single row of tubes, each equipped with wire fins, to optimize heat transfer efficiency. Commonly, a single row wire tube condenser features tubes with cross-sections of approximately 25 × 190 mm and fin heights of about 25 mm, delivering reliable and effective cooling performance.
Key Takeaways
- Single row wire tube condensers use wire fins on tubes to boost heat transfer and reduce energy loss, making cooling systems more efficient.
- Their compact design lowers air resistance and pressure drop, saving energy and fitting well in tight spaces like refrigerators and air conditioners.
- High-quality materials like copper and aluminum ensure durability and strong heat exchange, while adjustable tube and wire spacing optimize performance.
Single row wire tube condenser? How It Works
Basic Operating Principle
A single row wire tube condenser? operates by transferring heat from the refrigerant inside its tubes to the surrounding air. The design features a single row of tubes, each wrapped with wire fins. These fins increase the surface area, allowing more efficient heat dissipation. The refrigerant enters the condenser as a high-pressure vapor. As it flows through the tubes, it releases heat to the wire fins, which then transfer this heat to the air moving across the condenser.
The structure of the single row wire tube condenser? ensures that air flows smoothly over the tubes and fins. This arrangement reduces resistance to airflow and enhances cooling performance. The wire fins create turbulence, which improves the contact between air and the tube surface. This process accelerates heat removal from the refrigerant.
Tip: The single row design minimizes pressure drop, making it ideal for applications where energy efficiency and compact size are important.
The following table summarizes key technical data and performance metrics validated by computational and experimental studies:
| Design Parameter | Effect on Performance | Quantitative Data |
|---|---|---|
| Tube Shape (Kammtail vs Circular) | Kammtail tube reduces pressure drop and increases heat transfer | 19% lower pressure drop, 9% higher heat transfer coefficient |
| Fin Pitch | Smaller fin pitch increases pressure drop and decreases heat transfer | Pressure drop increase: 32.9–97%, Heat transfer decrease: 4.7–11.7% |
| Number of Tube Rows | Studied for 4 or 5 rows | Included in parametric analysis |
| Tube Arrangement | Inline and staggered arrangements analyzed | Included in parametric analysis |
| Performance Metric | Improvement/Change | Validation Details |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer Coefficient | Increased by 5.6–12.2% | Numerical results agree with experiments within <10% deviation |
| Static Pressure Drop | Reduced by 7–20.4% | Validated by experimental data with <10% deviation |
| Air Flow Rate | Reduced by 30% | Confirmed by experimental validation |
| Condenser Volume | Decreased by 20% | Supported by numerical and experimental results |
These findings confirm that the single row wire tube condenser? achieves high heat transfer efficiency with lower pressure drop, supporting its use in modern refrigeration systems.
Heat Exchange Process
The heat exchange process in a single row wire tube condenser? begins when hot, pressurized refrigerant vapor enters the tubes. As the vapor moves through the tubes, it contacts the inner walls, which are cooled by the surrounding wire fins. The wire fins, exposed to ambient air, absorb heat from the tubes and release it into the environment.
Empirical studies show that the single row design delivers excellent heat exchange performance. Numerical simulations and experimental measurements of the overall heat transfer coefficient (U) match closely, with differences of only 2.5-3%. This agreement validates the accuracy of the design models. Researchers have compared various heat exchanger configurations and found that innovative designs, such as those with snake motion outlines, achieve higher heat transfer coefficients than traditional uniform tube arrangements. The increased turbulence and secondary flows created by these geometries enhance convective heat transfer. As the Reynolds number rises, the overall heat transfer coefficient increases for all configurations, but the snake motion design consistently outperforms the uniform design.
The single row wire tube condenser? stands out for its ability to maximize heat transfer while minimizing energy loss. This efficiency makes it a preferred choice for applications where space, energy savings, and reliable performance are critical.
Single row wire tube condenser? Features and Construction

Materials and Design
Manufacturers select high-quality materials for single row wire tube condenser? construction to ensure durability and optimal heat transfer. Copper and aluminum often serve as the primary materials for tubes and fins. Copper provides excellent thermal conductivity, while aluminum offers a lightweight structure and resistance to corrosion. Research highlights the importance of key design parameters such as wire diameter, tube diameter, wire pitch, and tube pitch. These factors directly influence the condenser’s performance.
Engineers conduct experiments in wind tunnels to simulate real-world airflow conditions. They use advanced simulation tools like ANSYS Fluent to analyze how air moves around the wires and tubes. The studies show that even small changes in wire or tube diameter can impact heat transfer efficiency. Staggered wire arrangements, compared to tandem setups, improve heat transfer by up to 22%. This improvement results from better airflow distribution and reduced shadowing effects.
Note: Radiation heat transfer can contribute between 3% and 11% of the total heat transfer, depending on air velocity.
Size and Configuration
Single row wire tube condensers come in various sizes to fit different applications. The configuration typically features a single row of tubes, each wrapped with wire fins. Engineers adjust the tube and wire spacing to optimize airflow and maximize surface area for heat exchange. The most common configurations use a cross-flow arrangement, where air moves perpendicular to the tubes and wires.
| Parameter | Typical Range | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Tube Diameter | 6–10 mm | Affects heat transfer rate |
| Wire Diameter | 0.5–2 mm | Influences fin efficiency |
| Wire Pitch | 2–5 mm | Alters airflow resistance |
| Tube Pitch | 15–25 mm | Controls condenser size |
Manufacturers tailor these dimensions to meet specific cooling requirements. The flexibility in size and configuration allows the single row wire tube condenser? to serve a wide range of refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
Single row wire tube condenser? Advantages and Applications
Main Advantages
A single row wire tube condenser? offers several notable benefits in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. The design maximizes heat transfer efficiency by increasing the surface area exposed to airflow. Copper and aluminum materials provide excellent thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. The single row layout reduces pressure drop, which improves energy efficiency and lowers operational costs. Staggered wire arrangements further enhance heat transfer, with studies showing an 18–22% improvement compared to tandem setups. The compact structure allows for easy installation in limited spaces, making it suitable for modern equipment.
Tip: Engineers can optimize performance by adjusting wire diameter, tube diameter, and spacing, as confirmed by over 700 parametric analyses in industrial research.
Potential Drawbacks
While the single row wire tube condenser? delivers high efficiency, engineers must carefully select geometric parameters to match specific application needs. Free stream velocity significantly influences heat transfer performance. Incorrect sizing or arrangement may reduce effectiveness. Regular maintenance ensures optimal operation and longevity.
Common Applications
Single row wire tube condensers see widespread use across various industries. Typical applications include:
- Domestic refrigerators and freezers, where compact size and reliable cooling are essential.
- Air-cooled condenser systems in power plants, which help reduce water consumption compared to wet cooling methods.
- Industrial refrigeration units, where forced convection and optimized airflow are critical.
- Air conditioning systems for residential and commercial buildings.
Industry data shows that wire-on-tube condensers are often positioned perpendicular to airflow, reflecting common setups. Experimental and numerical studies validate their performance, with less than 10% error between predicted and measured results. These condensers play a vital role in both domestic and industrial cooling solutions.
A Single row wire tube condenser? stands out for its efficient heat transfer, compact design, and reliable performance. Engineers often select this condenser for applications requiring space-saving solutions and energy efficiency. Common uses include refrigerators, air conditioners, and industrial cooling systems.
- Unique structure maximizes airflow.
- Preferred for modern refrigeration needs.
FAQ
What materials do manufacturers use for single row wire tube condensers?
Manufacturers often use copper for tubes and aluminum for fins. These materials provide excellent heat transfer and resist corrosion.
How does a single row wire tube condenser improve energy efficiency?
The single row design reduces pressure drop. This feature allows systems to use less energy while maintaining effective cooling performance.
Where do engineers commonly install single row wire tube condensers?
Engineers install these condensers in refrigerators, air conditioners, and industrial cooling systems. The compact design fits well in limited spaces.