Author:
-
Position:
General Manager of Foreign Trade Department, Taojun Refrigeration -
Professional Experience:
Engaged in international trade within the refrigeration industry since 2004.
Expert in brand strategy and omni-channel marketing, having led three multi-million yuan projects that boosted brand exposure by over 200%.
-
Core Competencies:
Proficient in data analysis and user growth strategies.
Skilled in SEO/SEM and social media management tools.
Experienced in cross-departmental collaboration and team leadership.
-
Philosophy:
"Data-driven decisions, creativity-powered branding." Committed to achieving business value and user experience excellence through refined operations. -
Vision:
Eager to collaborate with partners to explore emerging market opportunities and set industry benchmark cases.
Contact Us to Find More Products
The Copper Accumulator Explained Why Your HVAC Company Needs It Now
A Copper Accumulator is a vital component in HVAC systems. It effectively manages refrigerant flow. This essential device protects the system's most critical component, the compressor. It prevents damaging liquid refrigerant from entering the compressor. This liquid can cause severe mechanical stress. Understanding the copper accumulator for hvac company operations is crucial. This knowledge ensures system longevity and peak efficiency. It directly contributes to an HVAC company's operational success.
Key Takeaways
- A copper accumulator protects your HVAC compressor. It stops liquid refrigerant from causing damage.
- Copper is best for accumulators. It moves heat well and resists rust.
- The accumulator helps your compressor last longer. It prevents liquid from breaking parts.
- It makes your HVAC system work better. This saves energy and money.
- A copper accumulator helps meet new energy rules. It works with new types of refrigerants.
- Install accumulators correctly. This ensures they work well and last a long time.
- Regular checks keep the accumulator working. This prevents big problems later.
What is a Copper Accumulator for HVAC Company Operations?
Defining the Refrigerant Accumulator
A refrigerant accumulator is a crucial component in vapor compression refrigeration cycles. It acts as a protective buffer for the system's compressor. This device ensures only vaporized refrigerant reaches the compressor.
Purpose in the Refrigeration Cycle
The primary purpose of a refrigerant accumulator is to prevent liquid refrigerant from entering the compressor. This protection is vital. Liquid refrigerant can cause severe damage, known as liquid slugging. An accumulator also improves system efficiency. It ensures a continuous flow of refrigerant to the evaporator. This continuous flow optimizes heat transfer. Furthermore, it stabilizes system operation. Maintaining proper refrigerant levels extends the HVAC system's lifespan.
Essential Design Characteristics
Refrigerant accumulators typically feature a cylindrical shell. They have an inlet connection at the top and an outlet connection near the bottom. An internal U-tube or dip tube extends from the top inlet to the bottom of the accumulator. This design facilitates the separation of liquid and vapor refrigerant.
The Advantage of Copper in Accumulator Construction
Copper offers significant benefits in accumulator construction. Its material properties enhance both performance and durability.
Superior Thermal Conductivity
Copper possesses superior thermal conductivity. This property allows for efficient heat exchange within the accumulator. It helps vaporize any trapped liquid refrigerant. This process ensures only gas enters the compressor. Consider the thermal conductivity values:
| Material/Model | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
|---|---|
| Aluminum (Industry Standard) | 237 |
| Copper (Base) | 380 |
| Copper Alloy (Advanced) | 400 |
| Copper (Standard) | 385 |
| Copper (Base Model) | 385 |
| Copper (Advanced Model) | 442 |
| Copper (Pro Model) | 500 |
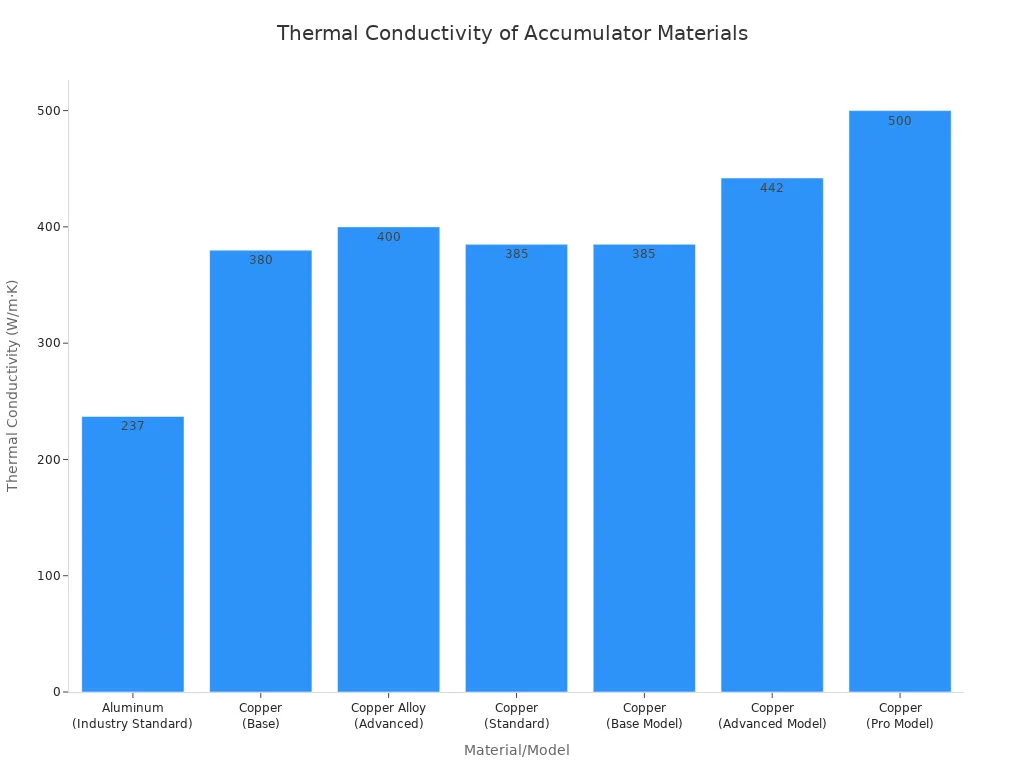
Copper's high thermal conductivity significantly outperforms aluminum. This characteristic makes copper an ideal material for accumulators.
Enhanced Corrosion Resistance
Copper also exhibits enhanced corrosion resistance. This resistance is crucial in various refrigerant environments. Copper alloys, such as C12200, possess inherent corrosion resistance. However, long-term exposure to refrigerants like R-134a, R-410A, or CO₂ can still lead to localized corrosion. Pitting corrosion can occur when negative ions attack copper's protective oxide film. This forms a corrosion-driven battery. Pits can progress through the copper thickness, causing pinholes and refrigerant leaks. Formicary corrosion, caused by oxygen, water, and organic acids, forms microscopic tunnels. This also leads to pinholes and leaks. Galvanic corrosion happens when dissimilar metals, like copper and aluminum, contact in an electrolyte. The more active metal corrodes faster. Despite these challenges, copper remains a robust choice for a copper accumulator for hvac company systems.
Key Internal Components and Their Functions
Understanding the internal components helps explain how accumulators function.
Refrigerant Inlet and Outlet
The refrigerant inlet is typically at the top of the accumulator. It receives a mixture of liquid and vapor refrigerant from the evaporator. The outlet, usually a U-tube or dip tube, draws vaporized refrigerant from the top section. This ensures only gas proceeds to the compressor.
Oil Return Orifice Mechanism
A small orifice or hole is located at the bottom of the U-tube. This mechanism allows oil, which separates from the refrigerant, to return to the compressor. The orifice ensures a controlled return of oil. This prevents oil from accumulating in the accumulator. It also maintains proper compressor lubrication.
How a Copper Accumulator Works to Protect Your HVAC System
A copper accumulator plays a critical role in safeguarding an HVAC system. It actively prevents damage to the compressor. This protection ensures the system operates reliably and efficiently.
Preventing Liquid Refrigerant Floodback to the Compressor
The accumulator acts as a crucial buffer. It stops liquid refrigerant from reaching the compressor, a common cause of system failure.
Liquid-Vapor Separation Process
The accumulator receives a mixture of liquid and vapor refrigerant from the evaporator. Inside the accumulator, gravity causes the heavier liquid refrigerant to settle at the bottom. The lighter refrigerant vapor rises to the top. This physical separation is fundamental to its protective function. The design ensures only vapor proceeds to the compressor.
Controlled Refrigerant Vaporization
An accumulator's primary role prevents liquid refrigerant from reaching the compressor. It also assists in returning oil to the compressor. Internally, it features a metered orifice designed for oil return. This orifice also atomizes liquid refrigerant before it returns to the compressor. The accumulator is mostly filled with refrigerant vapor. A U-bend with a small opening at the bottom facilitates oil return. An opening near the top allows vaporized refrigerant to return to the compressor. This controlled vaporization process protects the compressor from harmful liquid slugging.
Ensuring Consistent Oil Return for Compressor Lubrication
Proper lubrication is vital for compressor longevity. The copper accumulator actively manages oil circulation.
Oil Trapping and Metering
Refrigerant carries a small amount of compressor oil throughout the system. When this mixture enters the accumulator, the oil, being heavier than the refrigerant vapor, settles at the bottom with any liquid refrigerant. A small orifice or U-tube at the bottom of the accumulator meters this trapped oil. It ensures a controlled, steady return to the compressor. This prevents oil from accumulating in the accumulator, which would starve the compressor.
Maintaining Optimal Lubrication
The consistent return of oil ensures the compressor always receives adequate lubrication. This prevents excessive wear on moving parts. Optimal lubrication reduces friction and heat. It significantly extends the compressor's operational life. Without this mechanism, oil could remain trapped in the evaporator, leading to compressor damage.
The Operational Flow of Refrigerant Through the Accumulator
The accumulator dynamically manages refrigerant conditions. It ensures stable system performance.
Dynamic Pressure and Temperature Management
As refrigerant enters the accumulator, it experiences changes in pressure and temperature. The accumulator helps stabilize these conditions before the refrigerant reaches the compressor. It allows liquid refrigerant to vaporize gradually. This process prevents sudden pressure drops or surges that could stress the compressor.
Stabilizing Refrigerant Conditions
The accumulator acts as a temporary reservoir. It smooths out fluctuations in refrigerant flow. This stabilization ensures a consistent supply of vaporized refrigerant to the compressor. Consistent conditions lead to more efficient and reliable system operation. It minimizes wear and tear on critical components.
Why Your HVAC Company Needs a Copper Accumulator Now: Core Benefits
A copper accumulator offers significant advantages for HVAC companies. It directly impacts system longevity, operational efficiency, and overall reliability. Integrating this component into HVAC systems provides a competitive edge and ensures customer satisfaction.
Extending Compressor Lifespan and Reliability
The compressor represents the heart of any HVAC system. Protecting this critical component directly translates to extended system lifespan and enhanced reliability. A copper accumulator plays a pivotal role in this protection.
Eliminating Liquid Slugging Damage
Liquid refrigerant entering the compressor, known as liquid slugging, causes severe damage. This phenomenon occurs when liquid refrigerant, instead of vapor, reaches the compressor. Compressors are designed to pump refrigerant in vapor form; liquid refrigerant acts as a solid mass. When liquid enters, it can bend and break suction valves. This liquid also washes away lubrication, leading to scoring of cylinder walls and pistons. The piston, unable to compress liquid, hits this solid mass, causing hydraulic lock. This impact drives the liquid against suction and discharge valves, potentially smashing valve plates. Broken valve plate pieces can fall into the cylinder, leading to piston damage. Severe liquid accumulation can hydraulically lock the piston, breaking the connecting rod or crankshaft.
Liquid slugging, often caused by excessive expansion valve opening, leads to instantaneoushydraulic shocks exceeding 5MPa within the compressor. This phenomenon is responsible for over 35% of compressor failures attributed to mechanical issues, significantly increasing repair costs and energy consumption. Eliminating this issue directly prevents these hydraulic shocks and the associated mechanical stress.
A copper accumulator effectively prevents these damaging events. It ensures only vaporized refrigerant reaches the compressor, thereby eliminating the risk of liquid slugging.
Reducing Mechanical Stress and Wear
By preventing liquid slugging, the copper accumulator significantly reduces mechanical stress on compressor components. This reduction in stress minimizes wear and tear on pistons, valves, connecting rods, and crankshafts. The consistent flow of vaporized refrigerant ensures the compressor operates under its intended conditions. This stable operation avoids sudden impacts and excessive friction. Consequently, the compressor experiences fewer breakdowns and requires less frequent maintenance, leading to a longer operational life.
Boosting HVAC System Efficiency and Performance
Beyond protection, a copper accumulator actively contributes to the overall efficiency and performance of HVAC systems. It optimizes refrigerant flow and prevents energy waste.
Optimizing Refrigerant Flow Dynamics
The accumulator helps maintain optimal refrigerant flow dynamics throughout the system. It ensures a steady supply of vapor to the compressor and manages the return of oil. This optimization involves several factors:
- Subcooling Optimization: Cooling refrigerant below its condensation temperature increases cooling capacity and can improve cycle efficiency. However, excessive subcooling might lead to increased pressure drop and reduced compressor efficiency.
- Superheating Optimization: Heating refrigerant vapor above its evaporation temperature prevents compressor damage. While essential, excessive superheating can decrease cooling capacity and increase compressor work, negatively impacting efficiency. Maintaining an optimal degree (typically 5-10°C) is crucial.
- Refrigerant Charge Management: An optimal refrigerant charge is vital for maximizing system efficiency. Undercharging reduces cooling capacity and increases compressor work, while overcharging can cause liquid slugging and reduced heat transfer effectiveness.
Optimizing refrigerant flow dynamics through 'Optimal loading control' can lead to a significant improvement in the Coefficient of Performance (COP). For instance, an air conditioning system demonstrated a 17% increase in COP, rising from 5.2 to 6.1, by implementing such control strategies. This improvement highlights the direct impact of proper flow management on system efficiency.
Preventing Energy Waste and Inefficiency
An HVAC system operating with optimized refrigerant flow consumes less energy. The copper accumulator prevents inefficiencies caused by fluctuating refrigerant conditions. Without an accumulator, liquid refrigerant can flood the evaporator, reducing its heat transfer capability. This forces the compressor to work harder and longer to achieve the desired cooling or heating, leading to increased energy consumption. By ensuring proper vaporization and consistent flow, the accumulator helps the system operate at its peak efficiency, preventing unnecessary energy waste.
Enhancing Overall System Durability and Uptime
For any HVAC company, system durability and uptime are crucial for customer satisfaction and profitability. A copper accumulator significantly contributes to both.
Minimizing Costly Downtime and Repairs
By extending compressor lifespan and boosting efficiency, the copper accumulator directly minimizes costly downtime and repairs. Fewer compressor failures mean fewer emergency service calls and less time spent on extensive repairs. This translates into substantial savings for the HVAC company and less inconvenience for clients. The reliability provided by a robust copper accumulator for hvac company operations reduces operational expenses and improves service delivery.
Ensuring Consistent and Stable Operation
A system equipped with a copper accumulator operates more consistently and stably. It handles variations in load and ambient conditions more effectively. This stability ensures the system delivers reliable heating or cooling performance without unexpected interruptions. Consistent operation builds customer trust and enhances the reputation of the HVAC company for providing dependable solutions.
Meeting Evolving Industry Standards and Demands
The HVAC industry constantly evolves. New regulations and technological advancements shape its future. HVAC companies must adapt to remain competitive and compliant. A copper accumulator helps systems meet these changing requirements.
Adapting to New Refrigerant Types
The HVAC industry faces a significant transition. Environmental concerns drive the phase-out of high Global Warming Potential (GWP) refrigerants. Older refrigerants like R-22 and R-410A are being replaced. New, lower GWP alternatives are emerging. These include R-32, R-454B, R-290 (propane), and R-1234yf. Each new refrigerant possesses unique thermodynamic properties. These properties can affect system operation.
For example, some new refrigerants may have different pressure-temperature characteristics. This can increase the risk of liquid refrigerant returning to the compressor. Others might interact differently with compressor oils. This impacts oil return efficiency. A copper accumulator provides a critical buffer. It effectively manages these variations. The accumulator ensures only vaporized refrigerant reaches the compressor. This protects the compressor from liquid slugging, regardless of the refrigerant type. It also facilitates consistent oil return. This adaptability makes the copper accumulator an essential component. It helps HVAC systems safely integrate new refrigerants. This ensures long-term operational reliability.
Compliance with Energy Efficiency Regulations
Energy efficiency remains a top priority for regulators and consumers. Governments worldwide implement stricter energy efficiency standards. Examples include SEER2 (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio 2) and EER2 (Energy Efficiency Ratio 2) in the United States. These regulations demand higher performance from HVAC equipment. Systems must deliver more cooling or heating output for less energy input.
Inefficiencies directly impact a system's energy rating. Liquid refrigerant entering the compressor forces it to work harder. This wastes energy. Poor oil return can also reduce compressor efficiency. A copper accumulator directly addresses these issues. It ensures the compressor operates under optimal conditions. The accumulator prevents liquid slugging. It also guarantees proper lubrication. This optimized operation reduces energy consumption. It allows the HVAC system to achieve higher efficiency ratings. By integrating a copper accumulator for hvac company systems, businesses can confidently meet stringent energy efficiency regulations. This also offers customers more energy-efficient and cost-effective solutions.
Practical Applications of the Copper Accumulator for HVAC Company Systems
Copper accumulators are essential components across various HVAC and refrigeration systems. They ensure reliable operation and protect critical equipment. HVAC companies integrate these devices into diverse applications. This integration enhances system performance and longevity.
Integration in Residential HVAC Units
Residential HVAC units benefit significantly from copper accumulators. These devices protect compressors from liquid refrigerant damage. This protection is crucial for homeowner comfort and system durability.
Heat Pump Systems
Heat pump systems operate in both heating and cooling modes. This dual functionality often leads to varying refrigerant conditions. During defrost cycles or rapid changes in ambient temperature, liquid refrigerant can return to the compressor. A copper accumulator effectively separates this liquid. It ensures only vapor enters the compressor. This prevents liquid slugging and extends the heat pump's lifespan.
Central Air Conditioners
Central air conditioners also rely on copper accumulators. These units experience fluctuating loads. For example, a sudden drop in indoor temperature demand can cause liquid refrigerant to accumulate. The accumulator acts as a buffer. It prevents liquid floodback to the compressor. This maintains consistent cooling performance. It also safeguards the compressor from mechanical stress.
Role in Commercial Refrigeration Systems
Commercial refrigeration demands high reliability and precise temperature control. Copper accumulators are indispensable in these demanding environments. They support continuous operation and protect valuable inventory.
Walk-in Coolers and Freezers
Walk-in coolers and freezers operate continuously. They maintain stable low temperatures. Frequent door openings or product loading can cause refrigerant fluctuations. A copper accumulator manages these changes. It ensures a steady supply of vapor to the compressor. This prevents liquid from damaging the compressor. It also helps maintain consistent cooling.
Display Cases and Chillers
Display cases and chillers are common in supermarkets and restaurants. They require precise temperature management. Copper accumulators prevent liquid refrigerant from reaching the compressor. This is especially important during peak usage or defrost cycles. The accumulator ensures efficient operation. It protects the compressor from wear. This minimizes costly downtime for businesses.
Industrial HVAC and Process Cooling Applications
Industrial applications involve large-scale systems and critical processes. Here, the reliability of HVAC equipment is paramount. Copper accumulators play a vital role in these complex setups.
Large-Scale Chiller Systems
Large-scale chiller systems cool entire buildings or industrial processes. These systems handle significant refrigerant volumes. They operate under diverse load conditions. A copper accumulator protects the large compressors in these chillers. It prevents liquid floodback. This ensures continuous cooling capacity. It also avoids expensive repairs and production interruptions.
Specialized Process Cooling
Specialized process cooling applications often involve extreme temperatures or precise control. These systems are critical for manufacturing or data centers. The copper accumulator provides an essential layer of protection. It manages refrigerant flow. It prevents liquid from damaging sensitive compressors. This ensures the stability and efficiency of vital industrial processes.
Common Issues and Best Practices for Copper Accumulator Maintenance
Maintaining copper accumulators ensures the longevity and efficiency of HVAC systems. Understanding potential issues and implementing best practices helps prevent costly repairs and system downtime.
Identifying Signs of Accumulator Malfunction
Recognizing the symptoms of a malfunctioning accumulator allows for timely intervention. This prevents further damage to the HVAC system.
Compressor Damage Indicators
A malfunctioning accumulator directly impacts the compressor. The accumulator's primary role ensures only moisture-free, gaseous refrigerant enters the compressor. If the accumulator malfunctions, liquid refrigerant or moisture can enter the compressor. This leads to significant damage. Water reacts with refrigerant, forming corrosive acids. Liquid refrigerant causes hydraulic lock or other mechanical failures within the compressor. Technicians often observe specific signs indicating compressor damage linked to accumulator issues. These include rattling sounds when the AC operates. While this can also indicate a bad compressor, it suggests loose or damaged parts within a malfunctioning accumulator.
System Performance Degradation Symptoms
Beyond direct compressor damage, a faulty accumulator manifests through various system performance issues. An AC system not blowing as cold as it should indicates a problem. A clogged accumulator prevents proper cooling, indirectly stressing the compressor as it tries to compensate. Refrigerant leaks also signal a malfunctioning accumulator. A faulty accumulator allows pressurized refrigerant to escape, leading to low refrigerant levels. This condition overworks and damages the compressor.
Proper Installation Techniques for Optimal Function
Correct installation is paramount for a copper accumulator's effective operation and lifespan.
Correct Orientation and Placement
Install accumulators vertically. This orientation allows gravity to effectively separate liquid refrigerant from vapor. Place the accumulator in the suction line, between the evaporator and the compressor. This strategic placement ensures it captures any unvaporized liquid refrigerant before it reaches the compressor.
Brazing and Connection Guidelines
Proper brazing techniques are crucial for secure, leak-free connections. Use appropriate brazing alloys and nitrogen purging during the brazing process. Nitrogen prevents oxidation inside the tubing, which can create scale and contaminate the system. Ensure all connections are tight and free from leaks to maintain system integrity and refrigerant charge.
Routine Inspection and Care for Longevity
Regular inspection and care extend the life of the copper accumulator and the entire HVAC system.
Visual Integrity Checks
Periodically inspect the accumulator for external signs of damage. Look for corrosion, dents, or any evidence of refrigerant leaks around connections. Address any visible issues promptly to prevent further degradation.
Monitoring System Pressure Drops
Monitor system pressure drops across the accumulator. Significant pressure drops indicate a potential blockage or restriction within the accumulator. This condition impedes refrigerant flow and reduces system efficiency. Address these issues to maintain optimal system performance.
Selecting the Right Copper Accumulator for Your HVAC Company Needs
Choosing the correct copper accumulator is crucial for optimal HVAC system performance and longevity. HVAC companies must consider several factors. These factors include system specifications, product quality, and long-term value. Making an informed decision ensures reliable operation and customer satisfaction.
Sizing and Capacity Matching for System Performance
Proper sizing of a copper accumulator directly impacts system efficiency and compressor protection. An incorrectly sized accumulator can lead to performance issues.
Aligning with System BTU/Ton Requirements
HVAC professionals must match the accumulator's capacity to the system's BTU or tonnage requirements. An accumulator too small may not effectively separate liquid refrigerant. This leaves the compressor vulnerable. An accumulator too large can cause excessive pressure drop. This reduces system efficiency. Manufacturers provide sizing charts. These charts help select the appropriate accumulator based on system capacity.
Considering Refrigerant Type and Charge
The type of refrigerant used also influences accumulator selection. Different refrigerants have varying densities and flow characteristics. These properties affect how liquid and vapor separate within the accumulator. The system's refrigerant charge also plays a role. Ensure the accumulator can handle the system's full charge without becoming overwhelmed. This ensures effective protection for the compressor.
Importance of Quality and Manufacturer Reputation
The quality of a copper accumulator directly correlates with its performance and durability. Partnering with reputable manufacturers is essential.
Adherence to Material Standards
High-quality accumulators use premium copper. This copper adheres to strict industry material standards. This ensures superior thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. Inferior materials can lead to premature failure. This compromises system integrity. A well-constructed copper accumulator for hvac company operations provides lasting protection.
Certifications and Performance Testing
Reputable manufacturers subject their accumulators to rigorous testing. They also obtain relevant industry certifications. These certifications confirm product quality and safety.
Here are common certifications for quality accumulators:
- ISO
- CE
- RoHS
Some models offer additional certifications:
| Model | Certifications |
|---|---|
| Base Model | CE |
| Advanced Model | CE + RoHS |
| Pro Model | CE + RoHS + UL |
These certifications indicate the product meets specific performance and environmental standards. They provide assurance of reliability.
Evaluating Cost-Benefit and Long-Term Value
The initial purchase price is only one aspect of accumulator selection. HVAC companies must consider the overall cost-benefit.
Initial Investment vs. Operational Savings
A higher-quality copper accumulator may have a greater upfront cost. However, it offers significant long-term operational savings. It extends compressor life. It also reduces maintenance calls and energy consumption. These savings often outweigh the initial investment. This makes it a more economical choice over the system's lifespan.
Warranty and Technical Support
Evaluate the manufacturer's warranty and technical support. A strong warranty indicates confidence in product quality. Reliable technical support ensures quick assistance for installation or troubleshooting. This minimizes downtime and enhances operational efficiency for HVAC companies.
The copper accumulator stands as an indispensable component for safeguarding HVAC systems. It actively protects the compressor, the system's most vital part. This device offers significant immediate and long-term value for HVAC companies in today's competitive market. Proactive adoption of copper accumulators ensures:
- Enhanced system reliability
- Improved operational efficiency
- Future-proof HVAC operations
Companies secure lasting performance and customer satisfaction by integrating this crucial technology.
FAQ
What is the primary function of a copper accumulator in an HVAC system?
A copper accumulator prevents liquid refrigerant from entering the compressor. It ensures only vaporized refrigerant reaches this critical component. This protection safeguards the compressor from severe damage, known as liquid slugging.
Why is copper preferred for accumulator construction?
Copper offers superior thermal conductivity. This property efficiently vaporizes liquid refrigerant. Copper also provides enhanced corrosion resistance. These characteristics contribute to the accumulator's durability and effective operation.
What risks does an HVAC system face without a copper accumulator?
Without an accumulator, liquid refrigerant can flood the compressor. This causes liquid slugging, leading to mechanical damage. It also washes away lubrication. This significantly shortens the compressor's lifespan and increases repair costs.
How does a copper accumulator improve system efficiency?
It optimizes refrigerant flow dynamics. The accumulator ensures consistent vapor supply to the compressor. This prevents energy waste from inefficient operation. It allows the system to achieve higher energy efficiency ratings.
Are copper accumulators necessary for all types of HVAC systems?
Copper accumulators are highly beneficial for many HVAC and refrigeration systems. They are particularly crucial for heat pumps and systems with fluctuating loads. They protect the compressor and enhance overall system reliability.
What are key maintenance practices for copper accumulators?
Regular visual inspections are important for damage or leaks. Monitoring system pressure drops helps identify blockages. Proper installation, including correct orientation and brazing, also ensures optimal function and longevity.
How does a copper accumulator benefit an HVAC company directly?
It extends compressor lifespan, reducing costly repairs and downtime. It boosts system efficiency, leading to satisfied customers. This enhances overall system durability and helps meet evolving industry standards.