Author:
-
Position:
General Manager of Foreign Trade Department, Taojun Refrigeration -
Professional Experience:
Engaged in international trade within the refrigeration industry since 2004.
Expert in brand strategy and omni-channel marketing, having led three multi-million yuan projects that boosted brand exposure by over 200%.
-
Core Competencies:
Proficient in data analysis and user growth strategies.
Skilled in SEO/SEM and social media management tools.
Experienced in cross-departmental collaboration and team leadership.
-
Philosophy:
"Data-driven decisions, creativity-powered branding." Committed to achieving business value and user experience excellence through refined operations. -
Vision:
Eager to collaborate with partners to explore emerging market opportunities and set industry benchmark cases.
Contact Us to Find More Products
How to Audit ISO 9001 Wire Tube Condenser Factories: 7-Step Supplier Checklist

Audits play a vital role in maintaining quality and ensuring compliance in manufacturing environments. In wire tube condenser factories, where precision and consistency are critical, audits help identify areas for improvement and ensure adherence to industry standards. A structured 7-step checklist simplifies this process. It provides a systematic approach to evaluating suppliers, ensuring their production methods meet both ISO 9001 requirements and customer expectations. By adopting such a framework, businesses can enhance product reliability and foster stronger supplier relationships.
Key Takeaways
- Set clear goals for the audit that match your business needs.
- Look at important areas like quality checks and machine upkeep in wire tube condenser factories.
- Make success rules to check how well the audit works and track progress.
- Do detailed checks on documents to find problems before visiting the site.
- Check how things are made and machines are used during site visits to follow ISO 9001 rules.
- Write down what you find with proof and helpful tips to stay clear and responsible.
- Plan fixes for problems with clear steps and deadlines to solve them.
- Work well with suppliers by talking openly and giving regular feedback to keep improving.
Step 1: Define Audit Objectives
Align Objectives with Business Goals
Defining clear audit objectives begins with aligning them to the organization’s business goals. This ensures that the audit process addresses relevant risks and supports strategic priorities. For example, if a company aims to expand its market presence, the audit should evaluate risks related to regulatory compliance and operational efficiency. By focusing on these areas, auditors can provide actionable insights that strengthen the company’s ability to achieve its objectives.
Aligning audit objectives with business goals offers several benefits:
- It ensures the audit process targets critical risks and controls.
- It allows auditors to allocate resources effectively and prioritize their efforts.
- It provides assurance that strategic initiatives are supported and risks are managed.
To achieve this alignment, auditors should:
- Communicate with management to understand the organization’s strategic goals.
- Identify key risks tied to these goals, such as customer satisfaction or market competition.
- Focus audit efforts on evaluating these risks to assess the effectiveness of strategies.
This approach ensures that audits in wire tube condenser factories contribute to both operational excellence and long-term business success.
Identify Key Focus Areas for Wire Tube Condenser Factories
Wire tube condenser factories require audits tailored to their unique manufacturing processes. Key focus areas include quality control, equipment maintenance, and compliance with ISO 9001 standards. Auditors should also examine the factory’s ability to meet customer specifications and maintain consistent production quality. These focus areas are critical because they directly impact product reliability and customer satisfaction.
Additionally, auditors should assess the factory’s supply chain management and its approach to handling raw materials. Effective supply chain practices ensure that production schedules remain uninterrupted and that materials meet required standards. By concentrating on these areas, auditors can identify potential weaknesses and recommend improvements that enhance overall efficiency.
Set Measurable Success Criteria
Measurable success criteria provide a benchmark for evaluating the audit’s effectiveness. These criteria should be specific, actionable, and aligned with the factory’s operational goals. For instance, success could be measured by the percentage of compliance with ISO 9001 requirements or the reduction in production defects over a defined period.
Auditors should document these criteria before starting the audit. Examples of measurable criteria include:
- Achieving 95% compliance with quality management standards.
- Reducing equipment downtime by 10% within six months.
- Improving on-time delivery rates to 98% or higher.
Setting clear benchmarks ensures that the audit delivers tangible outcomes. It also helps stakeholders understand the value of the audit process and its role in driving continuous improvement.
Step 2: Develop Audit Criteria
Review ISO 9001:2015 Requirements for Manufacturing
ISO 9001:2015 outlines essential requirements for quality management systems in manufacturing. Auditors must familiarize themselves with these standards to develop effective audit criteria. Key elements include robust change control processes, systematic reviews during design stages, and verification and validation procedures. These practices ensure compliance with manufacturing requirements and enhance product reliability.
Auditors should also focus on personnel qualifications and training. Skilled workers contribute to consistent production quality and operational efficiency. Regular monitoring of processes and periodic audits further support compliance verification and continuous improvement.
Benefits of adhering to ISO 9001:2015 include:
- Enhanced trust with customers and partners.
- Improved operational efficiency by reducing waste and errors.
- Audit readiness, eliminating last-minute preparations.
By embedding these principles into audit criteria, wire tube condenser factories can align their operations with world-leading standards.
Customize Criteria for Wire Tube Condenser Factories
Wire tube condenser factories have unique manufacturing processes that require tailored audit criteria. Auditors should evaluate the factory’s ability to meet customer specifications and maintain consistent production quality. This includes assessing equipment maintenance schedules and quality control measures.
Supply chain management is another critical area. Factories must ensure raw materials meet required standards and production schedules remain uninterrupted. Auditors should examine procurement practices and inventory management systems to identify potential risks.
To customize criteria effectively, auditors can:
- Focus on factory-specific processes, such as wire tube bending and welding.
- Evaluate the integration of ISO 9001 principles into daily operations.
- Prioritize areas that directly impact product reliability and customer satisfaction.
Customized criteria allow auditors to address the unique challenges of wire tube condenser factories while supporting continuous improvement.
Incorporate Industry-Specific Standards and Best Practices
Industry-specific standards and best practices complement ISO 9001 requirements. Auditors should incorporate these elements into their criteria to ensure comprehensive evaluations. For example, standards related to refrigeration equipment manufacturing emphasize durability, energy efficiency, and environmental compliance.
Best practices include maintaining detailed documentation of design activities and conducting systematic reviews at predetermined stages. These practices improve traceability and accountability, reducing the likelihood of errors.
Auditors can also assess customer satisfaction metrics and procedures for continual improvement. Monitoring these areas helps factories identify opportunities for growth and innovation.
By integrating industry-specific standards and best practices, auditors can provide actionable recommendations that enhance the factory’s overall performance.
Step 3: Conduct a Desktop Audit
Collect and Review Supplier Documentation
A desktop audit begins with collecting and reviewing supplier documentation. This step provides a foundation for understanding the supplier's compliance with ISO 9001 standards and other relevant requirements. Auditors should request key documents, such as quality management system certifications, process flowcharts, and records of past inspections. These materials offer insights into the supplier's operational practices and adherence to quality standards.
Analyzing supplier documentation also helps identify discrepancies or outdated information. Studies show that nearly 30% of supplier data changes annually. This high rate of change can result in missing or inaccurate records, which may obscure critical compliance issues. To address this, auditors should cross-check supplier-provided data with third-party information. This approach ensures the accuracy of the review and minimizes the risk of overlooking potential problems.
Identify Potential Gaps in Compliance
The desktop audit phase is an opportunity to identify potential gaps in compliance before conducting an on-site evaluation. Auditors should compare the supplier's documentation against ISO 9001 requirements and any industry-specific standards. For wire tube condenser factories, this includes assessing records related to equipment maintenance, quality control, and raw material sourcing.
Common compliance gaps may include incomplete process documentation, missing certifications, or inconsistencies in quality records. Identifying these issues early allows auditors to prepare targeted questions and focus areas for the on-site audit. It also provides suppliers with an opportunity to address minor issues before they escalate into significant problems.
Prepare for On-Site Evaluation
The final step in the desktop audit involves preparing for the on-site evaluation. Auditors should use the findings from the documentation review to create a checklist of areas requiring further investigation. For example, if the desktop audit reveals inconsistencies in maintenance logs, the on-site audit should include a detailed inspection of equipment and maintenance practices.
Preparation also involves coordinating with the supplier to schedule the on-site visit. Auditors should communicate the scope of the evaluation and any specific documents or personnel required during the visit. This ensures a smooth and efficient audit process, allowing auditors to focus on verifying compliance and identifying opportunities for improvement.
By conducting a thorough desktop audit, auditors can streamline the on-site evaluation and enhance the overall effectiveness of the audit process. This step is crucial for ensuring that wire tube condenser factories meet quality and compliance standards.
Step 4: Perform an On-Site Audit
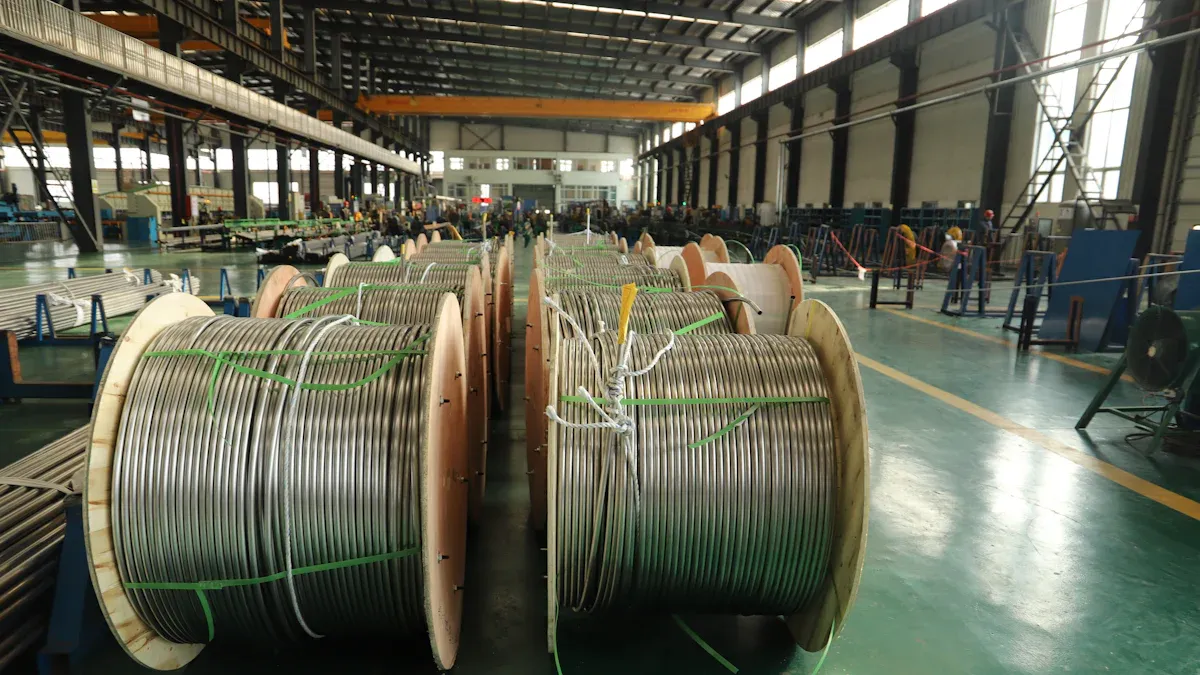

Inspect Manufacturing Processes and Equipment
Inspecting manufacturing processes and equipment is a critical step in the on-site audit. Auditors should observe production lines to ensure they operate efficiently and comply with ISO 9001 standards. Key areas to examine include the calibration of machinery, adherence to process controls, and the consistency of production outputs. These factors directly impact the quality and reliability of wire tube condensers.
Auditors should also evaluate the maintenance schedules and records for all equipment. Regular maintenance minimizes downtime and ensures machines function at optimal levels. For example, a well-maintained wire bending machine produces consistent results, reducing the likelihood of defects. By identifying any lapses in maintenance or operational inefficiencies, auditors can recommend actionable improvements.
Assess Facility Conditions and Safety Standards
Facility conditions play a significant role in maintaining product quality and ensuring worker safety. Auditors should assess the cleanliness and organization of the factory floor. A clutter-free environment reduces the risk of accidents and enhances operational efficiency. Proper storage of raw materials and finished products also prevents contamination or damage.
Safety standards must meet both regulatory requirements and industry best practices. Auditors should verify the availability of safety equipment, such as fire extinguishers and emergency exits. They should also check whether employees follow safety protocols, including wearing personal protective equipment (PPE). Factories that prioritize safety often experience fewer disruptions, leading to more consistent production schedules.
Interview Key Personnel on Quality Practices
Interviews with key personnel provide valuable insights into the factory's quality practices. Auditors should engage employees at various levels, from machine operators to quality control managers. These conversations help uncover practical challenges and identify areas for improvement. For instance:
- Interviews reveal deeper insights into daily processes.
- Employees often highlight challenges that may not appear in documentation.
- Open discussions allow auditors to understand operational realities.
Encouraging openness during interviews fosters trust and ensures accurate information. Auditors can use this data to assess whether employees understand and follow quality management procedures. This step also highlights the effectiveness of training programs and identifies opportunities for further development.
By combining observations, facility assessments, and employee interviews, auditors can gain a comprehensive understanding of the factory's operations. This holistic approach ensures that wire tube condenser factories meet quality and compliance standards while fostering continuous improvement.
Step 5: Analyze Audit Findings
Categorize Observations into Key Areas
Analyzing audit findings begins with organizing observations into key categories. This step helps auditors identify patterns and prioritize areas requiring immediate attention. Common categories include compliance, quality control, equipment maintenance, and employee training. Each category provides a framework for understanding the factory's strengths and weaknesses.
For example, compliance observations may highlight adherence to ISO 9001 standards, while quality control findings may reveal inconsistencies in production processes. Equipment maintenance issues often point to operational inefficiencies, and training gaps may indicate a need for improved workforce development. By grouping findings into these areas, auditors can streamline their analysis and focus on actionable insights.
A structured categorization process offers several benefits:
- It simplifies the identification of recurring issues.
- It ensures that critical areas receive adequate attention.
- It provides a clear roadmap for addressing non-compliance and inefficiencies.
Auditors should use this categorization to guide the next steps in the audit process, ensuring that all findings are addressed systematically.
Document Results with Evidence and Recommendations
Documenting audit results is essential for transparency and accountability. Auditors should record all observations, supported by evidence, and include actionable recommendations for improvement. This documentation serves as a reference for both the factory and stakeholders, ensuring that findings are clear and actionable.
| Evidence Description | Purpose |
|---|---|
| The auditor must document the procedures performed, evidence obtained, and conclusions reached with respect to relevant financial statement assertions. | Ensures compliance with standards and supports auditor's conclusions. |
| Audit documentation must include information relating to significant findings or issues that contradict the auditor's final conclusions. | Enhances transparency and accountability in the audit process. |
| The auditor must document significant findings or issues, actions taken to address them, and the basis for the conclusions reached. | Provides a comprehensive view of the audit process and supports compliance analysis. |
Detailed documentation ensures that all parties understand the audit's scope and outcomes. For example, auditors should include photographs of equipment, copies of maintenance logs, and summaries of employee interviews. Recommendations should address specific issues, such as updating maintenance schedules or enhancing quality control procedures.
Key principles for effective documentation include:
- Transparency in reporting deficiencies in internal controls.
- Addressing noncompliance with relevant regulations.
- Recording discrepancies in operational or quality records.
This approach ensures that the audit report becomes a valuable tool for driving improvements and maintaining compliance.
Share Findings with Stakeholders
Sharing audit findings with stakeholders fosters collaboration and accountability. Auditors should present their results in a clear and concise manner, using visual aids like charts or graphs to enhance understanding. Stakeholders, including factory management and external partners, rely on this information to make informed decisions.
Auditors should tailor their communication to the audience. For example, technical details may be necessary for factory managers, while high-level summaries may suffice for executives. Key points to include in the presentation are:
- A summary of compliance levels and identified gaps.
Step 6: Create a Corrective Action Plan

Address Non-Compliance Issues with Specific Actions
Corrective actions provide a structured approach to resolving non-compliance issues. Auditors should identify specific areas that require immediate attention and propose targeted solutions. For example, if equipment maintenance records reveal inconsistencies, the factory should implement a standardized logging system to ensure accurate tracking. Similarly, if quality control processes fail to meet ISO 9001 standards, revising procedures and retraining staff can address these gaps effectively.
Focused corrective actions often lead to measurable improvements in supplier performance. Key benefits include:
- Implementation of Non-Conformance Reports (NCRs) and Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) plans reduced average call handling times by 15% within three months.
- Customer satisfaction scores increased by 20% over six months.
- Annual savings of $2.5 million were achieved due to enhanced efficiency and fewer penalties for non-compliance.
By addressing non-compliance issues with specific actions, factories can improve operational efficiency, enhance product quality, and strengthen customer trust.
Focus on Continuous Improvement Opportunities
Continuous improvement ensures long-term success for wire tube condenser factories. Auditors should identify opportunities that go beyond immediate corrective actions. For instance, introducing advanced equipment or automating repetitive tasks can enhance production efficiency. Regularly updating training programs ensures employees stay informed about best practices and industry standards.
Factories should also monitor trends in customer feedback and market demands. This data helps identify areas for innovation, such as developing energy-efficient condensers or improving product durability. Auditors can recommend strategies to integrate these improvements into the factory’s operations.
Continuous improvement fosters adaptability and resilience. Factories that prioritize innovation and efficiency often outperform competitors and maintain strong supplier relationships.
Assign Responsibilities and Deadlines
Assigning clear responsibilities ensures corrective actions are implemented effectively. Auditors should work with factory management to designate individuals or teams for each task. For example, the maintenance team can oversee equipment updates, while the quality control department handles process revisions.
Deadlines create accountability and keep improvement efforts on track. Auditors should recommend realistic timelines for each corrective action. For instance, updating maintenance logs might require two weeks, while retraining staff could take one month.
A structured plan with assigned responsibilities and deadlines ensures corrective actions are completed efficiently. This approach minimizes disruptions and supports continuous improvement in wire tube condenser factories.
Step 7: Monitor Supplier Progress
Conduct Follow-Up Audits to Verify Compliance
Follow-up audits play a crucial role in ensuring suppliers address non-compliance issues effectively. These audits validate whether corrective actions have been implemented and assess their impact on operational performance. By revisiting key areas identified in the initial audit, businesses can confirm that suppliers meet ISO 9001 standards and maintain consistent quality.
To measure the effectiveness of follow-up audits, organizations often rely on specific metrics and objectives. The table below highlights some common measurable outcomes:
| Measurable Outcome | Description |
|---|---|
| SMART Criteria | Establishes Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound objectives for audits. |
| Compliance Objective Example | Assess compliance with data integrity requirements by a specific deadline. |
| KPIs for Audit Program | Metrics such as % of planned audits completed and average time to close audit findings. |
| Corrective Action Plans | Defined timelines, responsibilities, and milestones for implementing audit recommendations. |
These metrics provide a structured framework for evaluating supplier progress. For example, tracking the percentage of completed audits ensures accountability, while monitoring the average time to close findings highlights areas for process improvement.
Foster Long-Term Collaboration with Suppliers
Building long-term relationships with suppliers enhances trust and promotes continuous improvement. Open communication during audits fosters mutual understanding and aligns supplier processes with business objectives. This collaborative approach encourages suppliers to view audits as opportunities for growth rather than mere compliance checks.
Several benefits arise from fostering collaboration:
- Open communication fosters mutual understanding and aligns supplier processes with business objectives.
- Two-way communication during audits encourages collaborative problem-solving and innovation.
- Regular audits build trust and respect, essential for long-term supplier relationships.
- Insights gained from audits enhance empathy and support between businesses and suppliers.
For instance, when suppliers actively participate in discussions about audit findings, they gain valuable insights into customer expectations. This shared understanding often leads to innovative solutions that benefit both parties. Over time, such partnerships strengthen supply chain resilience and improve overall performance.
Share Feedback to Drive Ongoing Improvement
Providing constructive feedback is essential for driving continuous improvement. Auditors should share their findings in a clear and actionable manner, highlighting both strengths and areas for enhancement. Feedback sessions should focus on solutions, offering practical recommendations that suppliers can implement to address identified gaps.
Regular feedback also creates a culture of accountability. Suppliers who receive consistent updates on their performance are more likely to prioritize quality and compliance. Additionally, feedback sessions provide an opportunity to celebrate achievements, reinforcing positive behaviors and motivating suppliers to maintain high standards.
By combining follow-up audits, collaboration, and feedback, businesses can ensure their suppliers remain aligned with quality objectives. This comprehensive approach not only strengthens supplier relationships but also supports long-term operational success.
The 7-step checklist offers a structured approach to auditing ISO 9001 wire tube condenser factories. It ensures thorough evaluations, leading to improved quality, compliance, and supplier relationships. A well-executed audit process reduces supplier defect rates by 50-70% and decreases lead times by 30-40%.
- Supplier scorecards track key metrics like on-time delivery.
- Regular performance reviews enable constructive feedback.
- Active monitoring fosters continuous improvement.
Adopting this checklist empowers businesses to enhance operational efficiency and build stronger partnerships, driving long-term success.
FAQ
What is the purpose of auditing ISO 9001 wire tube condenser factories?
Auditing ensures factories comply with ISO 9001 standards, maintain consistent quality, and meet customer expectations. It identifies areas for improvement and strengthens supplier relationships.
How often should audits be conducted?
Audits should occur annually or semi-annually, depending on the factory's performance and the complexity of its operations. Regular audits promote continuous improvement.
What documents are essential for a desktop audit?
Key documents include ISO 9001 certifications, process flowcharts, maintenance logs, and quality control records. These provide insights into compliance and operational practices.
Why is on-site auditing necessary?
On-site audits verify the accuracy of documentation and assess real-time manufacturing processes, equipment conditions, and employee adherence to quality standards.
How can factories prepare for an audit?
Factories should organize documentation, ensure equipment maintenance is up-to-date, and train employees on quality management practices. Preparation ensures a smoother audit process.
What are the benefits of follow-up audits?
Follow-up audits confirm corrective actions have been implemented and assess their effectiveness. They help maintain compliance and improve operational efficiency.
How do auditors ensure objectivity during evaluations?
Auditors rely on standardized criteria, evidence-based findings, and measurable benchmarks. This approach ensures fair and unbiased assessments.
Can audits improve supplier relationships?
Yes, audits foster collaboration by identifying improvement opportunities and aligning supplier practices with business goals. Stronger relationships lead to better performance and trust.