Author:
-
Position:
General Manager of Foreign Trade Department, Taojun Refrigeration -
Professional Experience:
Engaged in international trade within the refrigeration industry since 2004.
Expert in brand strategy and omni-channel marketing, having led three multi-million yuan projects that boosted brand exposure by over 200%.
-
Core Competencies:
Proficient in data analysis and user growth strategies.
Skilled in SEO/SEM and social media management tools.
Experienced in cross-departmental collaboration and team leadership.
-
Philosophy:
"Data-driven decisions, creativity-powered branding." Committed to achieving business value and user experience excellence through refined operations. -
Vision:
Eager to collaborate with partners to explore emerging market opportunities and set industry benchmark cases.
Contact Us to Find More Products
Finned Tube vs Wire Tube Condensers: Which Is Better for Commercial Refrigeration?
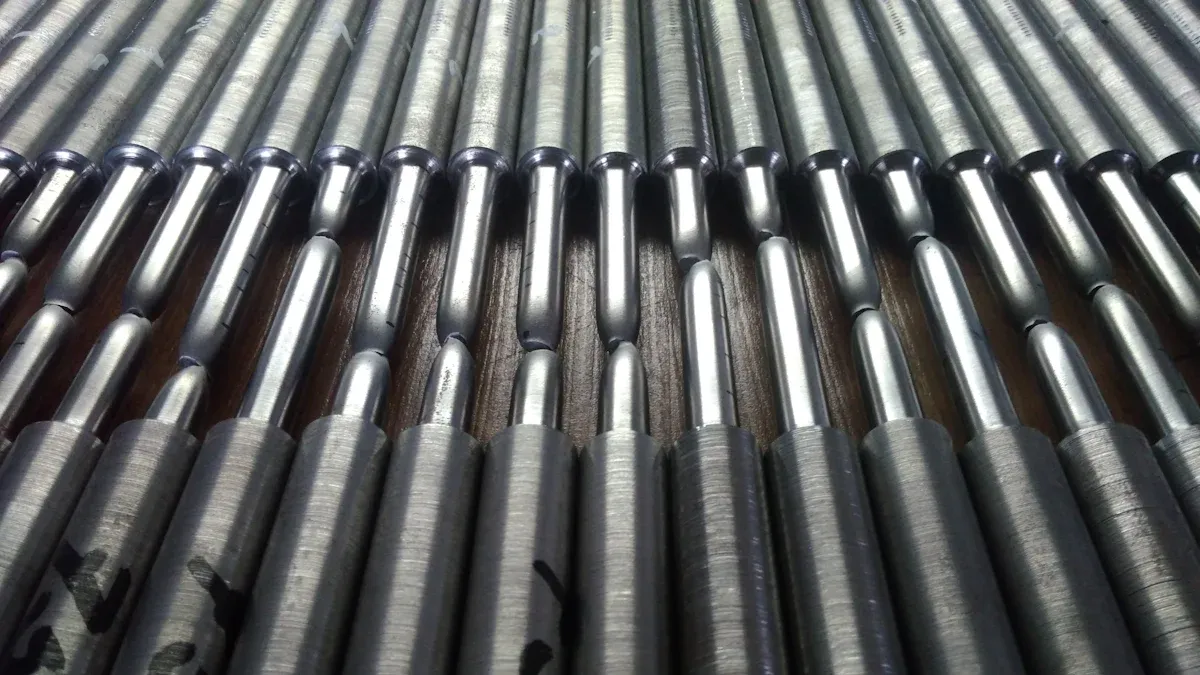

Efficient refrigeration systems rely on effective condenser designs. Finned tube condensers enhance heat transfer through a large surface area created by attached fins. Studies show these designs achieve superior performance, with coefficients of performance peaking when paired with optimal refrigerant quantities like 48–50 g of R600a. On the other hand, wire tube condensers use simple wire structures for heat dissipation, prioritizing affordability and ease of maintenance. A wire tube condenser comparison with finned tube counterparts reveals distinct advantages for different applications, making the choice dependent on operational priorities.
Key Takeaways
- Finned tube condensers move heat better, great for busy refrigeration needs.
- Wire tube condensers cost less and are simpler to care for.
- Both need upkeep; finned tubes need cleaning more often to work well.
- Pick the right one based on your needs; finned tubes are efficient, wire tubes save money and are easier.
- For businesses with less upkeep help, wire tubes with green refrigerants cut costs and help the planet.
Finned Tube Condensers

How They Work
Finned tube condensers operate by enhancing heat transfer through an extended surface area. Metal fins attached to the tubes increase the contact area between the refrigerant and the surrounding air, facilitating efficient heat dissipation. Air flows over the fins, absorbing heat from the refrigerant inside the tubes. This process ensures rapid cooling, making finned tube condensers ideal for applications requiring high thermal efficiency.
Studies on air-cooled condensers reveal that fouling, such as dust and sand accumulation, can impact performance. Mathematical modeling and experimental analysis have provided insights into fouling dynamics, enabling the development of cleaning schedules based on air mass velocity. The table below summarizes key findings:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Focus | Effects of fouling on heat transfer efficiency in air-cooled condensers. |
| Key Findings | Solid fouling from air affects performance; common types include dust, fluff, and sand. |
| Methodology | Mathematical modeling and experimental analysis of fouling dynamics. |
| Practical Application | Development of a methodology for determining cleaning periods based on air mass velocity. |
| Originality | New insights into solid fouling control and its impact on heat exchanger efficiency. |
Advantages
Finned tube condensers offer several benefits for commercial refrigeration. Their design maximizes heat transfer efficiency, ensuring optimal cooling performance even in high-demand environments. The extended surface area reduces the time required for heat dissipation, improving overall system reliability. These condensers also support a wide range of refrigerants, making them versatile for various applications. Their robust construction ensures durability, allowing them to withstand challenging operating conditions.
Disadvantages
Despite their efficiency, finned tube condensers may require regular maintenance to address fouling issues caused by airborne particles. Cleaning schedules based on air mass velocity can mitigate these challenges, ensuring consistent performance. Additionally, their initial cost may be higher compared to simpler designs like wire tube condensers. However, the long-term benefits often outweigh the upfront investment, especially for efficiency-focused applications.
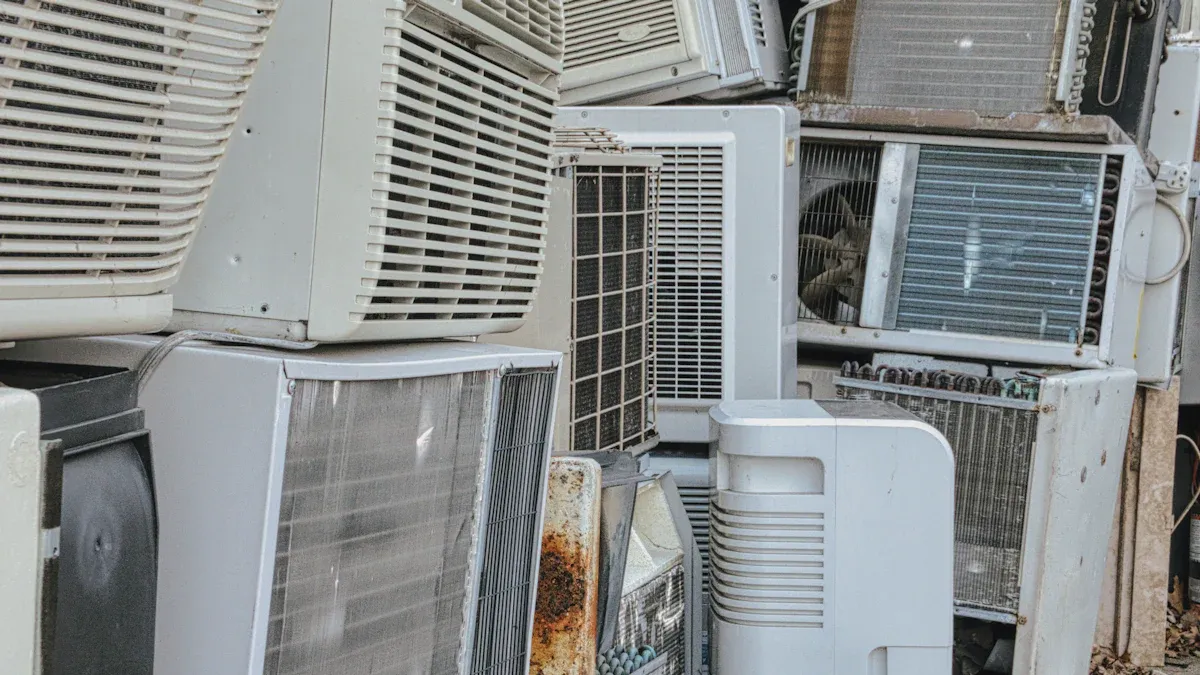
Wire Tube Condensers

How They Work
Wire tube condensers operate using a straightforward design. They consist of a series of metal wires arranged in a grid-like structure. These wires serve as the primary medium for heat dissipation. As refrigerant flows through the tubes, heat transfers to the wire grid. The surrounding air absorbs this heat, cooling the refrigerant effectively. This design relies on natural convection, where air movement occurs without mechanical assistance. The simplicity of this mechanism makes wire tube condensers a reliable choice for many commercial refrigeration systems.
Advantages
Wire tube condensers offer several notable benefits. Their simple construction ensures affordability, making them a cost-effective option for businesses with budget constraints. Maintenance is another significant advantage. The open design allows for easy cleaning and inspection, reducing downtime during servicing. These condensers also perform well in environments with moderate cooling demands, providing consistent results without requiring complex components. Their durability further enhances their appeal, as the sturdy wire structure withstands wear and tear over time.
Disadvantages
Despite their advantages, wire tube condensers have limitations. Their efficiency is lower compared to finned tube condensers, particularly in high-demand applications. The reliance on natural convection can result in slower heat dissipation, which may not meet the needs of systems requiring rapid cooling. Additionally, their performance can be affected by environmental factors such as dust accumulation, which may obstruct airflow. While maintenance is straightforward, regular cleaning is essential to maintain optimal functionality. A wire tube condenser comparison with finned tube designs highlights these trade-offs, emphasizing the importance of selecting the right condenser for specific operational needs.
Wire Tube Condenser Comparison with Finned Tube Condensers
Efficiency
Efficiency plays a critical role in determining the suitability of a condenser for commercial refrigeration. Finned tube condensers excel in this area due to their enhanced heat transfer capabilities. The fins increase the surface area, allowing faster and more effective cooling. This design supports high-demand applications, where rapid heat dissipation is essential for maintaining optimal refrigeration temperatures.
Wire tube condensers, on the other hand, rely on natural convection for heat dissipation. While this mechanism is sufficient for moderate cooling needs, it may struggle to match the performance of finned tube designs in high-volume environments. The simpler structure of wire tube condensers limits their ability to handle large thermal loads efficiently. Businesses prioritizing energy efficiency often lean toward finned tube condensers for their superior cooling performance.
Tip: For operations requiring consistent cooling under heavy loads, finned tube condensers are the preferred choice due to their higher efficiency.
Cost
Cost considerations often influence the choice between wire tube and finned tube condensers. Wire tube condensers stand out as the more affordable option. Their straightforward design reduces manufacturing expenses, making them accessible to businesses with budget constraints. Additionally, their lower upfront cost appeals to operations where initial investment is a primary concern.
Finned tube condensers, while more expensive initially, offer long-term value through their efficiency and durability. The higher cost reflects the advanced engineering and materials used in their construction. For businesses focused on minimizing operational costs over time, the improved energy efficiency of finned tube condensers can offset the initial expense.
| Condenser Type | Initial Cost | Long-Term Value |
|---|---|---|
| Wire Tube | Low | Moderate |
| Finned Tube | High | High |
Durability
Durability is another critical factor in the wire tube condenser comparison with finned tube condensers. Finned tube condensers feature robust construction designed to withstand challenging operating conditions. Their materials resist corrosion and wear, ensuring reliable performance over extended periods. This durability makes them suitable for environments where equipment faces frequent use or exposure to harsh elements.
Wire tube condensers also offer solid durability, thanks to their simple and sturdy design. The wire grid structure resists physical damage and wear, making it a reliable choice for applications with moderate cooling demands. However, finned tube condensers often outperform wire tube designs in terms of longevity, especially in high-demand scenarios.
Note: While both options provide durability, finned tube condensers are better suited for operations requiring heavy-duty performance over time.
Maintenance
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of both finned tube and wire tube condensers. Each type has unique maintenance requirements due to differences in design and operational mechanisms.
Finned Tube Condensers
Finned tube condensers require regular cleaning to maintain optimal performance. Dust, dirt, and other airborne particles can accumulate on the fins, reducing heat transfer efficiency. Cleaning schedules should be based on the operating environment and air quality. For example, systems in dusty or industrial areas may need more frequent cleaning.
Key maintenance practices for finned tube condensers include:
- Surface Cleaning: Use compressed air or a soft brush to remove debris from the fins. Avoid using high-pressure water, as it may damage the delicate fins.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect the fins for bending or damage. Bent fins can obstruct airflow and reduce efficiency. Fin combs can help straighten bent fins.
- Corrosion Prevention: Apply anti-corrosion coatings to protect the metal surfaces, especially in humid or corrosive environments.
Tip: Establish a maintenance log to track cleaning and inspection schedules. This practice ensures consistent upkeep and helps identify recurring issues.
Wire Tube Condensers
Wire tube condensers are easier to maintain due to their open design. The simple structure allows for quick cleaning and inspection, making them a practical choice for businesses prioritizing low-maintenance equipment. However, regular upkeep is still necessary to prevent performance degradation.
Recommended maintenance steps for wire tube condensers include:
- Debris Removal: Use a vacuum or a damp cloth to clean the wire grid. This process prevents dust buildup, which can obstruct airflow and reduce cooling efficiency.
- Visual Inspection: Check for signs of wear or damage to the wires. Replace any damaged components promptly to maintain functionality.
- Environmental Considerations: Position the condenser in a well-ventilated area to minimize exposure to contaminants like grease or oil, which can adhere to the wires.
Maintenance Comparison
The maintenance requirements for finned tube and wire tube condensers differ significantly. Finned tube condensers demand more attention due to their intricate design and susceptibility to fouling. In contrast, wire tube condensers offer a simpler maintenance routine, making them ideal for operations with limited technical resources.
| Aspect | Finned Tube Condensers | Wire Tube Condensers |
|---|---|---|
| Cleaning Frequency | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate |
| Ease of Cleaning | Moderate (requires care with fins) | High (open design simplifies it) |
| Inspection Requirements | Frequent (fins prone to damage) | Less Frequent |
| Maintenance Complexity | Higher | Lower |
Note: A wire tube condenser comparison with finned tube designs highlights the trade-off between maintenance complexity and performance. Businesses should weigh these factors when selecting a condenser type.
Recommendations for Commercial Refrigeration
High-Volume Applications
High-volume refrigeration systems demand condensers capable of handling substantial thermal loads efficiently. Finned tube condensers excel in these scenarios due to their advanced heat transfer capabilities. Their design maximizes the contact area between refrigerant and air, ensuring rapid cooling even under heavy operational demands.
The following table highlights key performance benefits of finned tube condensers in high-volume applications:
| Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced heat transfer | High liquid flow increases surface area contact with fins, improving heat transfer efficiency. |
| Reducing temperature gradient | High flow reduces residence time, leading to a smaller temperature difference between inlet and outlet. |
| Reduce heat loss | Faster heat transfer minimizes unnecessary heat loss, enhancing efficiency and reducing energy use. |
These features make finned tube condensers ideal for industries such as food storage, pharmaceuticals, and large-scale retail refrigeration. Their ability to maintain consistent cooling under heavy loads ensures product integrity and operational reliability.
Tip: Businesses operating in high-demand environments should prioritize finned tube condensers to optimize energy efficiency and cooling performance.
Cost-Sensitive Applications
Cost-sensitive operations often prioritize affordability without compromising basic functionality. Wire tube condensers provide a practical solution for businesses with budget constraints. Their simple construction reduces manufacturing costs, making them accessible to a wide range of industries.
Wire tube condensers perform well in environments with moderate cooling needs. Their reliance on natural convection eliminates the need for complex components, further reducing operational expenses. Maintenance costs remain low due to their open design, which simplifies cleaning and inspection.
Comparative studies on refrigerant types reveal additional cost-saving opportunities:
| Refrigerant Type | Energy Efficiency | Maintenance Costs | Carbon Footprint |
|---|---|---|---|
| R744 (CO2) | Superior | Lower | Reduced |
| R404a | Moderate | Higher | Increased |
| R449a | Moderate | Higher | Increased |
Wire tube condensers paired with energy-efficient refrigerants like R744 can further reduce operational costs while minimizing environmental impact.
Note: For businesses prioritizing affordability, wire tube condensers offer a cost-effective solution with reliable performance.
Low-Maintenance Applications
Low-maintenance refrigeration systems benefit from condensers designed for simplicity and durability. Wire tube condensers stand out in this category due to their straightforward design. The open wire grid structure allows for easy cleaning and inspection, reducing downtime during servicing.
Finned tube condensers, while requiring more frequent maintenance, can also be adapted for low-maintenance environments with proper planning. Anti-corrosion coatings and scheduled cleaning routines can extend their operational lifespan, ensuring consistent performance.
For businesses seeking minimal upkeep, wire tube condensers paired with refrigerants like R744 offer a compelling combination of low maintenance costs and energy efficiency. Their durability ensures reliable operation over time, making them suitable for applications with limited technical resources.
Tip: Operations with limited access to maintenance personnel should consider wire tube condensers for their ease of upkeep and long-term reliability.
Finned tube and wire tube condensers serve distinct purposes in commercial refrigeration. Finned tube condensers excel in efficiency due to their advanced heat transfer design, making them suitable for high-demand applications. Wire tube condensers, with their simpler construction, offer affordability and ease of maintenance, ideal for cost-sensitive or low-maintenance operations.
Recommendation: Businesses requiring consistent cooling under heavy loads should opt for finned tube condensers. For operations prioritizing budget or minimal upkeep, wire tube condensers provide a practical solution. Matching the condenser type to specific operational needs ensures optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
FAQ
What factors should businesses consider when choosing between finned tube and wire tube condensers?
Businesses should evaluate cooling efficiency, cost, durability, and maintenance requirements. High-demand applications benefit from finned tube condensers, while cost-sensitive or low-maintenance operations often prefer wire tube designs. Matching the condenser type to operational needs ensures optimal performance.
Are wire tube condensers suitable for high-volume refrigeration systems?
Wire tube condensers are less efficient in high-volume systems due to their reliance on natural convection. Finned tube condensers, with their enhanced heat transfer capabilities, are better suited for handling substantial thermal loads in demanding environments.
How often should finned tube condensers be cleaned?
Cleaning frequency depends on the operating environment. Systems in dusty or industrial areas may require monthly cleaning, while those in cleaner environments can follow quarterly schedules. Regular maintenance prevents fouling and ensures consistent performance.
Tip: Use a maintenance log to track cleaning intervals and identify recurring issues.
Can wire tube condensers handle environmentally friendly refrigerants like R744?
Yes, wire tube condensers are compatible with eco-friendly refrigerants like R744 (CO2). Pairing them with such refrigerants reduces operational costs and minimizes environmental impact, making them a sustainable choice for cost-sensitive applications.
Which condenser type offers better long-term value?
Finned tube condensers provide better long-term value due to their efficiency and durability. While their initial cost is higher, energy savings and reduced operational expenses often offset the investment. Wire tube condensers, however, remain a cost-effective option for moderate cooling needs.
Note: Consider total cost of ownership when evaluating long-term value.